|

Mental
Health is all about Mental health is a level of psychological well-being or an absence of mental illness. It is the "psychological state of someone who is functioning at a satisfactory level of emotional and behavioural adjustment". From the perspective of positive psychology or holism, mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life, and create a balance between life activities and efforts to achieve psychological resilience. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), mental health includes "subjective well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, inter-generational dependence, and self-actualization of one's intellectual and emotional potential, among others." The
WHO further states that the well-being of an individual is encompassed in the realization of their abilities, coping with normal stresses of life, productive work and contribution to their community. Cultural differences, subjective assessments, and competing professional theories all affect how "mental health" is defined.
According to the U.K. surgeon general (1999), mental health is the successful performance of mental function, resulting in productive activities, fulfilling relationships with other people, and providing the ability to adapt to change and cope with adversity. The term mental illness refers collectively to all diagnosable mental disorders—health conditions characterized by alterations in thinking, mood, or behavior associated with distress or impaired functioning.
A person struggling with their mental health may experience this because of stress, loneliness, depression, anxiety, relationship problems, death of a loved one, suicidal thoughts, grief, addiction, ADHD, Cutting, Self-harm, Self-Injury, burning, various mood disorders, or other mental illnesses of varying degrees, as well as learning disabilities. Therapists, psychiatrists, psychologists, social workers, nurse practitioners or physicians can help manage mental illness with treatments such as therapy, counseling, or medication.
Mental illnesses are more common than cancer, diabetes, or heart disease. Over 26 percent of all Americans over the age of 18 meet the criteria for having a mental illness. A WHO report estimates the global cost of mental illness at nearly $2.5 trillion (two-thirds in indirect costs) in 2010, with a projected increase to over $6 trillion by 2030.
Evidence from the World Health Organization suggests that nearly half of the world's population are affected by mental illness with an impact on their self-esteem, relationships and ability to function in everyday life. An individual's emotional health can also impact physical health and poor mental health can lead to problems such as substance abuse.
Maintaining good mental health is crucial to living a long and healthy life. Good mental health can enhance one's life, while poor mental health can prevent someone from living an enriching life. According to Richards, Campania, & Muse-Burke, "There is growing evidence that is showing emotional abilities are associated with prosocial behaviors such as stress management and physical health." Their research also concluded that people who lack emotional expression are inclined to anti-social behaviors (e.g., drug and alcohol abuse, physical fights, vandalism), which are a direct reflection of their mental health and suppress emotions. Adults and children with mental illness may experience social stigma, which can exacerbate the issues.
Mental health can be seen as an unstable continuum, where an individual's mental health may have many different possible values. Mental wellness is generally viewed as a positive attribute, even if the person does not have any diagnosed mental health condition. This definition of mental health highlights emotional well-being, the capacity to live a full and creative life, and the flexibility to deal with life's inevitable challenges. Some discussions are formulated in terms of contentment or happiness. Many therapeutic systems and self-help books offer methods and philosophies espousing strategies and techniques vaunted as effective for further improving the mental wellness. Positive psychology is increasingly prominent in mental health.
A holistic model of mental health generally includes concepts based upon anthropological, educational, psychological, religious and sociological perspectives, as well as theoretical perspectives from personality, social, clinical, health and developmental psychology.
The tripartite model of mental well-being views mental well-being as encompassing three components of emotional well-being, social well-being, and psychological well-being. Emotional well-being is defined as having high levels of positive emotions, whereas social and psychological well-being are defined as the presence of psychological and social skills and abilities that contribute to optimal functioning in daily life. The model has received empirical support across cultures. The Mental Health Continuum-Short Form (MHC-SF) is the most widely used scale to measure the tripartite model of mental well-being.
PREVENTION
Mental health is conventionally defined as a hybrid of absence of a mental disorder and presence of well-being. Focus is increasing on preventing mental disorders. Prevention is beginning to appear in mental health strategies, including the 2004 WHO report "Prevention of Mental Disorders", the 2008 EU "Pact for Mental Health" and the 2011 US National Prevention Strategy. Some commentators have argued that a pragmatic and practical approach to mental disorder prevention at work would be to treat it the same way as physical injury prevention.
Prevention of a disorder at a young age may significantly decrease the chances that a child will suffer from a disorder later in life, and shall be the most efficient and effective measure from a public health perspective. Prevention may require the regular consultation of a physician for at least twice a year to detect any signs that reveal any mental health concerns.
In
the case we are following where a man was convicted of rape
of a young girl, apart from the fact that the girl was "tightly
closed", there was also no signs of tearing of the fourchette, or
other trauma associated with digital penetration (without foreplay = dry).
The girl claimed regular assaults of this type that would have produced
scars and the like in 83% of cases, but there were no scars, a finding
which is clearly inconsistent with her claims. We wonder then about the
claimant's mental health and that of her mother, a community
psychiatric nurse with suicidal tendencies. We also wonder as the the
mental state of Dr Melanie Liebenberg, a so-called pediatric specialist
who must have known that the evidence she was giving to the Jury in this
case was flawed.
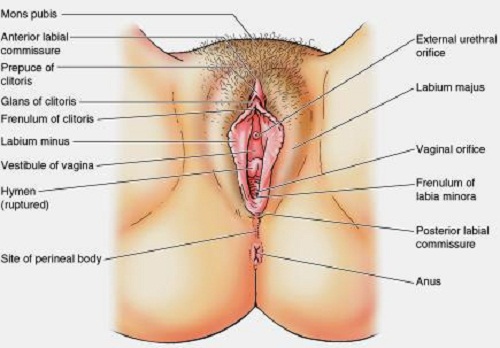
A
partial notch was found in the hymen, but it is now known that such
findings are normal. Tears and the like in the hymen are full width if
caused by trauma, leaving scar tissue, rather than partial (a smooth small
indentation) as in naturally occurring
features. This was not explained to the jury, who were left believing that
there was no explanation for the 'notch' other than penetrative sex, when
in fact it was a naturally occurring feature in all females of all ages.
Yet, an innocent man was sent to prison by the system. In this case the
so-called expert used her position of trust to mislead the Jury, by way of
helping the police to gain a conviction
of a dissident resident who was making waves as to this force failing
to investigate crime in Wealden
District Council. One way of neutralising political opponents is to
discredit them with a sexual allegation. After
that, nobody is likely to believe anything they say.
TREATMENT
Physical Activity
Physical activity is a very good way to help improve your mental health as well as your physical health. Playing sports, walking, cycling or doing any form of physical activity can trigger the production of endorphins. Endorphins are natural mood enhancers.
Activity therapies
Activity therapies, also called recreation therapy and occupational therapy, promote healing through active engagement. Making crafts can be a part of occupational therapy. Walks can be a part of recreation therapy. In recent years colouring has been recognised as an activity which has been proven to significantly lower the levels of depressive symptoms and anxiety in many studies.
Expressive therapies
Expressive therapies are a form of psychotherapy that involves the arts or art-making. These therapies include music therapy, art therapy, dance therapy, drama therapy, and poetry therapy. It has been proven that Music therapy is an effective way of helping people who suffer from a mental health disorder.
Meditation
The practice of mindfulness meditation has several mental health benefits, such as bringing about reductions in depression, anxiety and stress. Mindfulness meditation may also be effective in treating substance use disorders. Further, mindfulness meditation appears to bring about favorable structural changes in the brain.
The Heartfulness meditation program has proven to show significant improvements in the state of mind of health-care professionals. A study posted on the US National Library of Medicine showed that these professionals of varied stress levels were able to improve their conditions after this meditation program was conducted. They benefited in aspects of burnouts and emotional wellness.
People with anxiety disorders participated in a stress-reduction program conducted by researchers from the Mental Health Service Line at the W.G. Hefner Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Salisbury, North Carolina. The participants practiced mindfulness meditation. After the study was over, it was concluded that the "mindfulness meditation training program can effectively reduce symptoms of anxiety and panic and can help maintain these reductions in patients with generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, or panic disorder with agoraphobia."
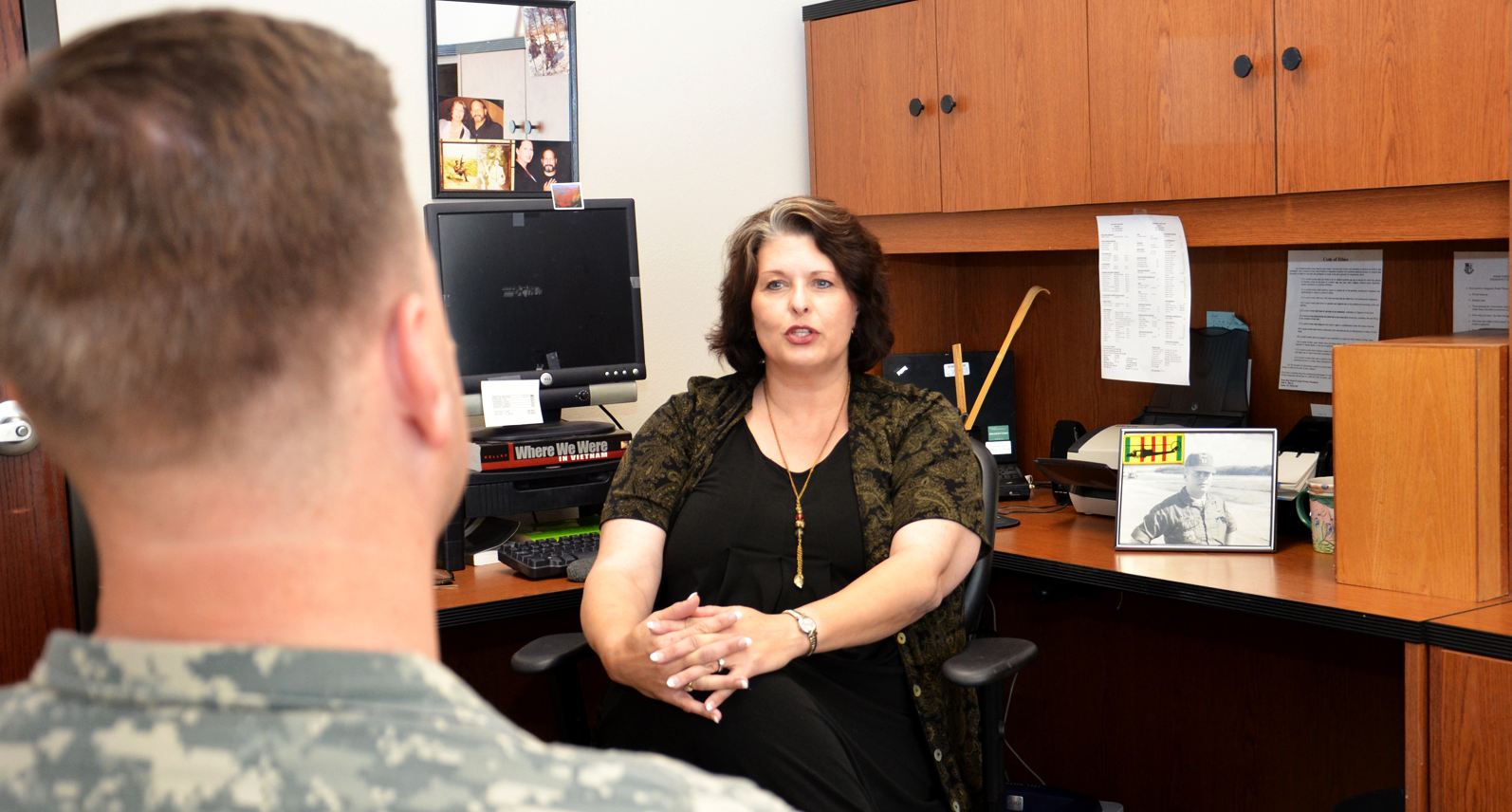

SOCIAL WORKERS
Social work in mental health, also called psychiatric social work, is a process where an individual in a setting is helped to attain freedom from overlapping internal and external problems (social and economic situations, family and other relationships, the physical and organizational environment, psychiatric symptoms, etc.). It aims for harmony, quality of life, self-actualization and personal adaptation across all systems. Psychiatric social workers are mental health professionals that can assist patients and their family members in coping with both mental health issues and various economic or social problems caused by mental illness or psychiatric dysfunctions and to attain improved mental health and well-being. They are vital members of the treatment teams in Departments of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences in hospitals. They are employed in both outpatient and inpatient settings of a hospital, nursing homes, state and local governments, substance abuse clinics, correctional facilities, health care services...etc.
In psychiatric social work there are three distinct groups. One made up of the social workers in psychiatric organizations and hospitals. The second group consists members interested with mental hygiene education and holding designations that involve functioning in various mental health services and the third group consist of individuals involved directly with treatment and recovery process.
In the United
States, social workers provide most of the mental health services. According to government sources, 60 percent of mental health professionals are clinically trained social workers, 10 percent are psychiatrists, 23 percent are psychologists, and 5 percent are psychiatric nurses.
Mental health social workers in Japan have professional knowledge of health and welfare and skills essential for person's well-being. Their social work training enables them as a professional to carry out Consultation assistance for mental disabilities and their social reintegration; Consultation regarding the rehabilitation of the victims; Advice and guidance for post-discharge residence and re-employment after hospitalized care, for major life events in regular life, money and self-management and in other relevant matters in order to equip them to adapt in daily life. Social workers provide individual home visits for mentally ill and do welfare services available, with specialized training a range of procedural services are coordinated for home, workplace and school. In an administrative relationship, Psychiatric social workers provides consultation, leadership, conflict management and work direction. Psychiatric social workers who provides assessment and
psychosocial interventions function as a clinician, counselor and municipal staff of the health centers.

1. You have a chronic fatigue and weakness.
2. Requests from colleagues or loved ones cause anger.
3. People on the verge of a breakdown are prone to self-criticism. They blame themselves for accepting the situation.
4. Excessive irritability is also inherent in people who are about to burst.
5. If you have the impression that you surround yourself with enemies and you have nowhere to hide, it is very likely that you’ll have a mental breakdown.
6. Words and actions that earlier did not draw any emotion, now are causing a painful reaction. Constantly you think that you are insulted and teased.
7. The breakdown often indicates a severe headache and indigestion.
8. Before a mental breakdown, people often suffer from insomnia and depression.
9. The sense of helplessness, characteristic of the person in front of a mental breakdown, it is usually accompanied by excessive fear, and sometimes persecution complex.
10. Due to problems with digestion, sometimes people lose weight.
REGIME
WITH MENTAL HEALTH ISSUES 1939 TO 1945
|

Adolf
Hitler
German
Chancellor
|

Herman
Goring
Reichsmarschall
|

Heinrich
Himmler
Reichsführer
|

Joseph
Goebbels
Reich Minister
|

Philipp
Bouhler SS
NSDAP
Aktion T4
|

Dr
Josef Mengele
Physician
Auschwitz
|
|

Martin
Borman
Schutzstaffel
|

Adolph
Eichmann
Holocaust
Architect
|

Rudolf
Hess
Commandant
|

Erwin
Rommel
The
Desert Fox
|

Karl
Donitz
Kriegsmarine
|

Albert
Speer
Nazi
Architect
|
CIVIL
SERVANTS WITH PERVERSE AGENDAS 1983 TO 2018
|

Ian
Kay
Assist.
Dist. Plan.
|

Charles
Lant
Chief
Executive
|

Victorio
Scarpa
Solicitor
|

Timothy
Dowsett
Dist.
Secretary
|

Christine
Nuttall
Solicitor
|

David
Phillips
Planning
|
|

Daniel
Goodwin
Chief
Executive
|

J
Douglas Moss
Policy
|

Kelvin
Williams
Dist.
Planning
|

Trevor
Scott
Solicitor
|

David
Whibley
Enforcement
|

Christine
Arnold
Planning
|
|

Chris
Bending
District
Planning
|

Beverley
Boakes
Legal
Secretary
|

Patrick
Coffey
Planning
|

Julian
Black
Planning
|

Ashley
Brown
Dist.
Planning
|

Derek
Holness
Former
CEO
|
Abbott
Trevor - Alcock
Charmain - Ditto - Arnold
Chris (Christine) - Barakchizadeh
Lesley - Paul Barker - Bending
Christopher
Black
Julian - Boakes Beverley - Bradshaw
Clifford - Brigginshaw
Marina - Brown
Ashley - Coffey
Patrick - Douglas
Sheelagh
Dowsett Timothy - Flemming
Mike - Forder Ralph - Garrett
Martyn - Goodwin Daniel
- Henham J - Holness
Derek
Hoy
Thomas - Johnson
Geoff - Kavanagh Geoff - Kay Ian - Kay
I. M.
- Barbara Kingsford - Lant Charles - Mercer
Richard
Mileman Niall - Moon
Craig - Moss Douglas, J. - Nuttall
Christine - Pettigrew Rex - Phillips
David - Scarpa
Victorio - Scott
Trevor
Kevin Stewart - Wakeford
Michael. - Whibley David - White,
George - Williams
Kelvin - Wilson Kenneth - White
Steve
HOME |
AFFORDABLE | CLIMATE
| DEVELOPERS | ECONOMY
| FLOOD | HISTORY
| HOMES LADDER
| MORALS
| POVERTY
| PROPERTY | SLAVERY
| TAXES | SLUMS |
VALUATIONS | WEALTH A
- Z INDEX
|





























